My system is as follows:
- Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS
- Mysql 5.7.22
Stop the mysql process:
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
Use mysqld_safe using the –skip-grant-tables option to start the process:
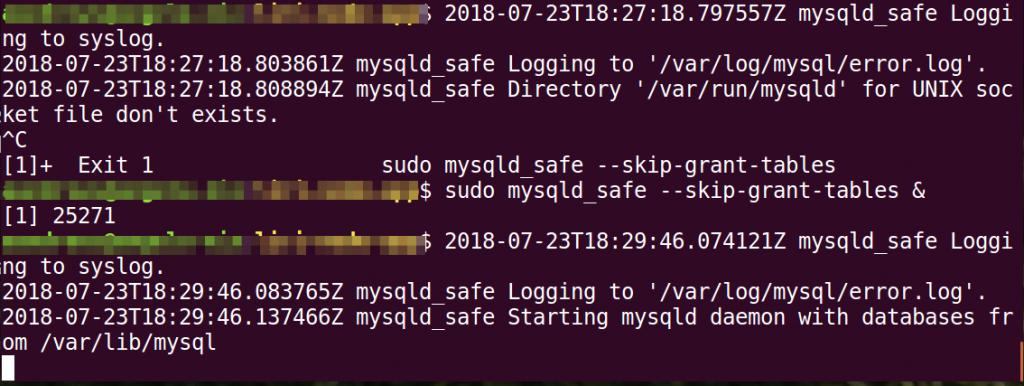
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
If you get an error about: mysqld_safe Directory ‘/var/run/mysqld’ for UNIX socket file doesn’t exist, check 2 things.
- If you have a /var/run/mysqld directory, if not, make one and change the permissions with chown.
- In the /etc/mysql/ directory, there is a file called, my.cnf open it and add the following:
sudo chown mysql:mysql /var/run/mysqld
[mysqld] port=3306 socket=/var/run/mysqld/mysql.sock
Save and close this file and re-run sudo mysqld_safe –skip-grant-tables &
You should see a message that reads: mysqld_safe Started mysqld daemon with databases from /var/lib/mysql
Open another terminal and log into mysql
mysql -u root
Now you can reset your password. Run these commands:
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> UPDATE user SET password=PASSWORD('pass123') WHERE user='root';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> quit
If you get an error when running the UPDATE user command that reads: ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column ‘password’ in ‘field list’, do this next.
Assuming this is for the mysql database:
mysql> use mysql; mysql> show tables;
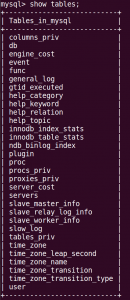
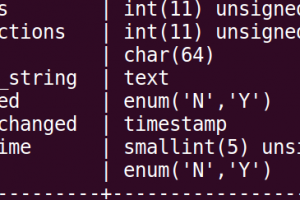
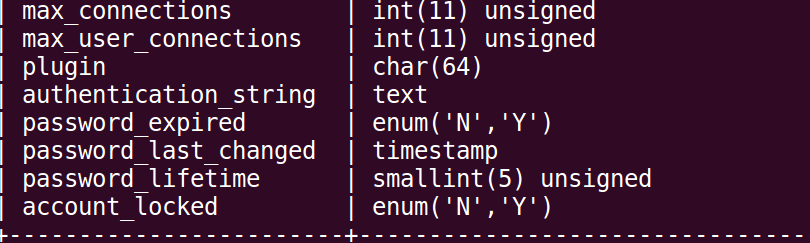
If you don’t see a row called password, but there is a user field, run this:
mysql> describe user;
There is a row called ‘authentication_string’ that holds the password.
You will need to run this command to reset the password. Just like the command above, but referencing the correct field in the user table.
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> UPDATE user SET authentication_string=PASSWORD('pass123') WHERE user='root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
quit
Log back in and test your new mysql password
mysql -u root -p