The MEM (Multipath Extension Module) by EqualLogic (EQL) handles path selection and load balancing to the storage array. Upon install, it will add another path selection policy called ‘dell_psp_eql_routed’ in addition to the 3 default policies. Using this PSP is ideal when you’re datastores reside on EQL since the module is written by EQL, it has been designed to perform more efficiently in regards to path selection and load balancing to the array.
Here is how I installed and configured MEM on my esxi hosts. I’m running ESXi 5.1 Update 1 with vSphere CLI installed on vCenter.
Prerequisite: Be sure to configure an iSCSI vSwitch for multipathing before installing MEM. Please read TR1075 for more information on how to configure the vSwitch.
Download MEM from EQL support site. Login is required. Review the release notes, TR1074 as well as the installation & user guide before proceeding.
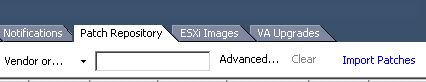
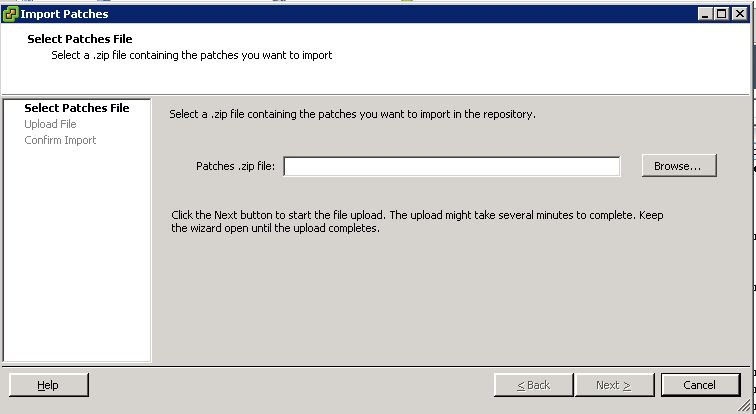
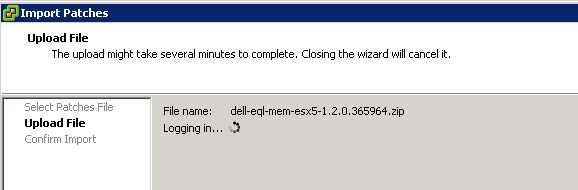
On the vCenter server, launch vCenter client. From the home screen, open Update Manager and click on the patch repository tab. Click import patches and browse to the MEM offline bundle zip and click next to upload.
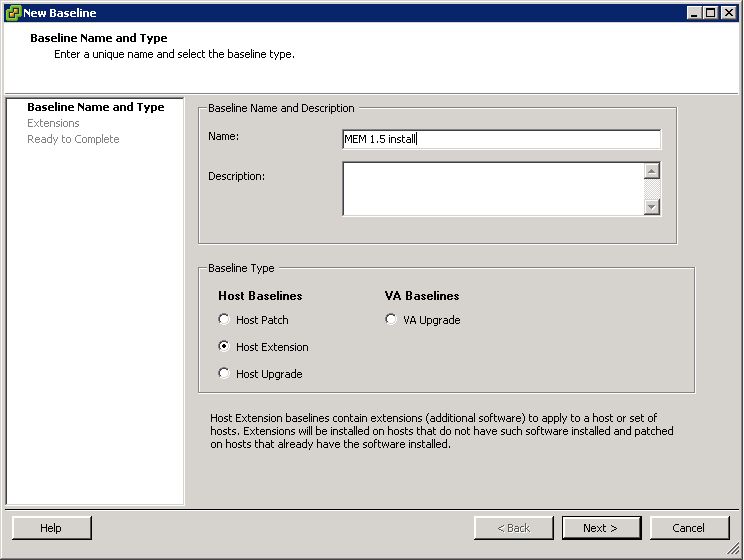
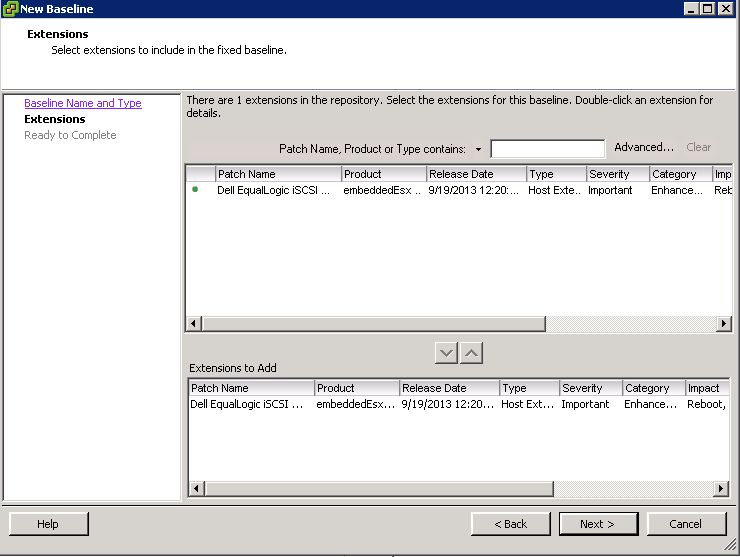
Next, create a baseline. Enter a name and description for your new baseline, select ‘Host Extension’ then click next.
Add the extension to the baseline. Click next.
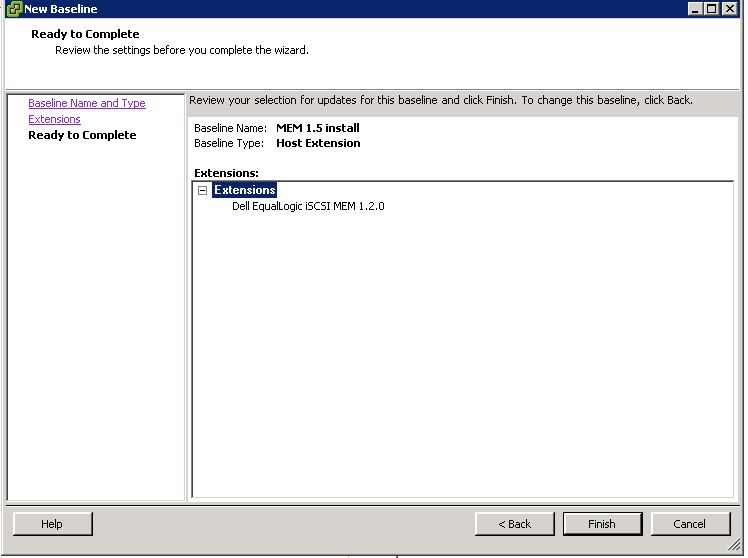
Review your setting and click finish.
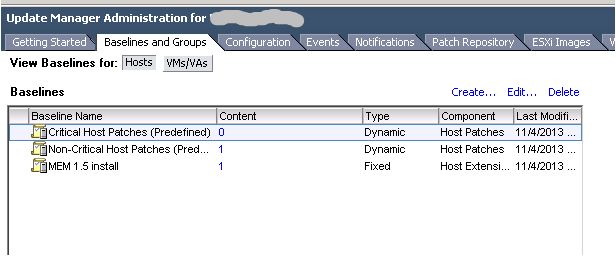
Your newly created baseline is now listed under the Baselines and Groups tab.
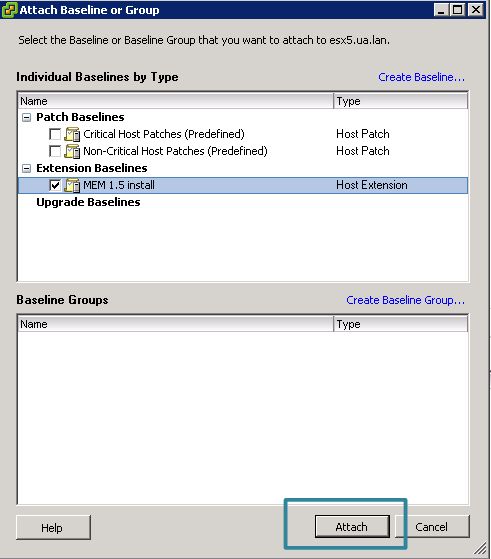
Now it’s time to install. Begin by putting your host into maintenance mode.Click the update manager tab of the host and click attach.
Check the box next to the MEM install and click attach.
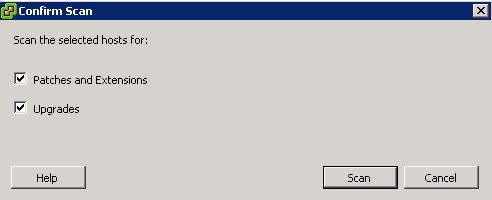
Highlight the attached baseline and click scan.
Confirm that you’re scanning for patches and extensions. Remove the check next to upgrades. Click scan.
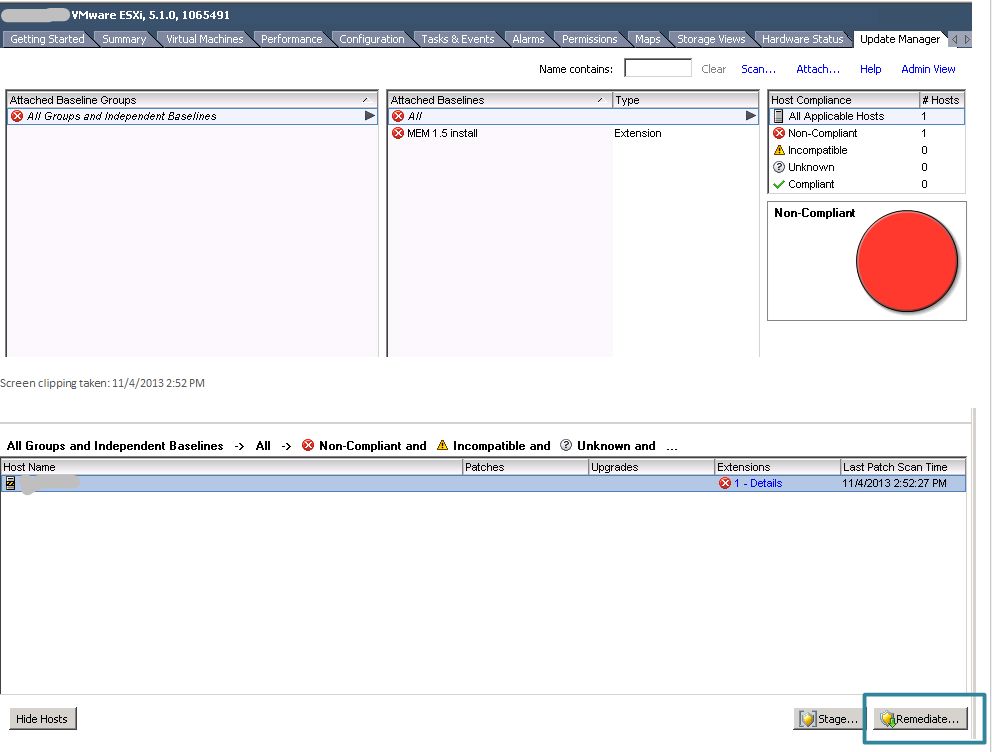
The host will now be labeled as non-compliant. Click remediate in the lower right corner.
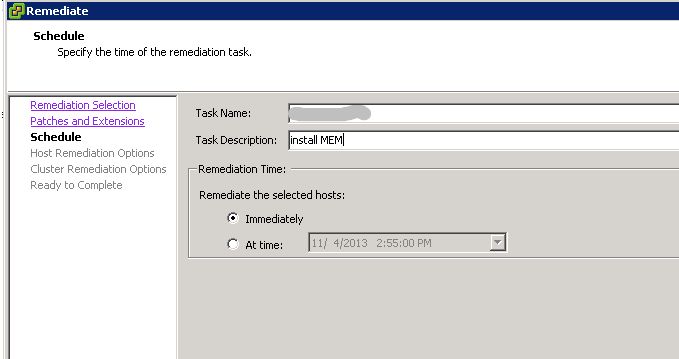
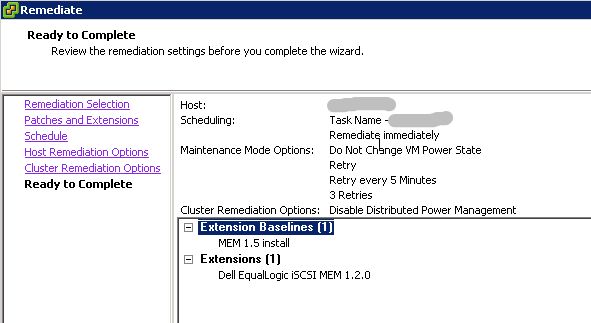
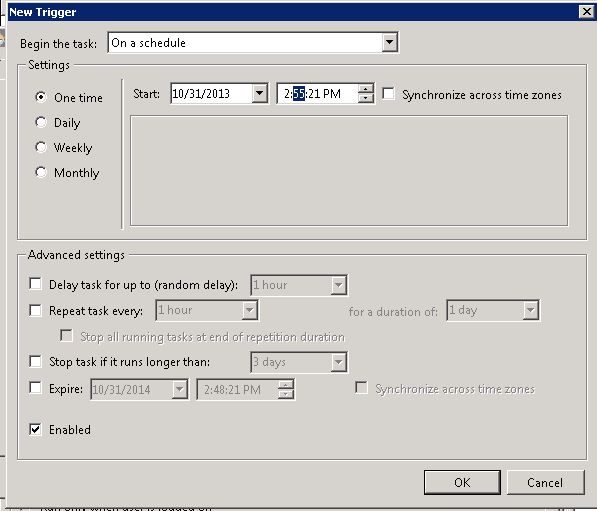
Click next twice in the remediate wizard if you’re accepting the defaults. On the schedule window, type in a new task name and description (optional) and select a remediation time. I did mine immediately, but this task can be scheduled for a later time. Click next.
Edit any host remediation options and click next. Edit any cluster remediation options and click next. Review your remediation settings and click finish.
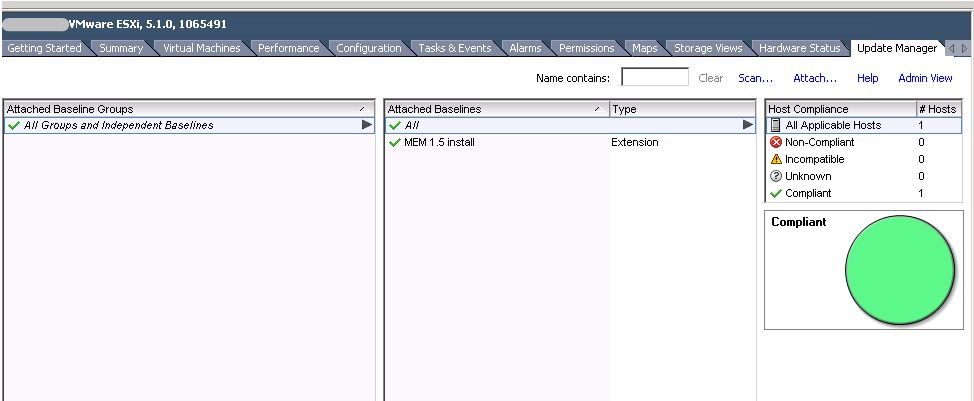
Monitor the recent tasks pane to see the status of the installation. Upon completion, the host will be listed as compliant in the update manager tab.
Reboot.
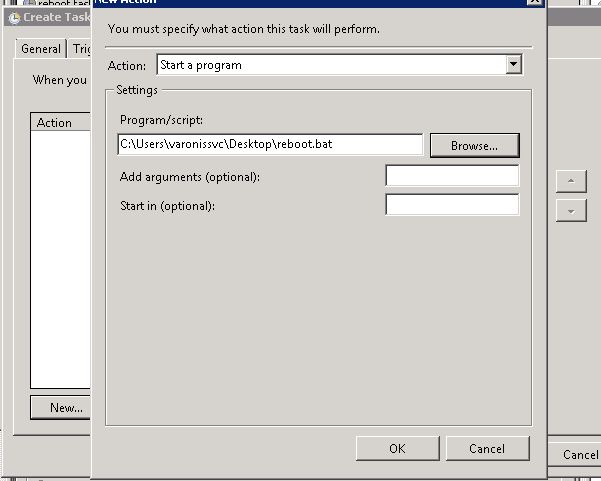
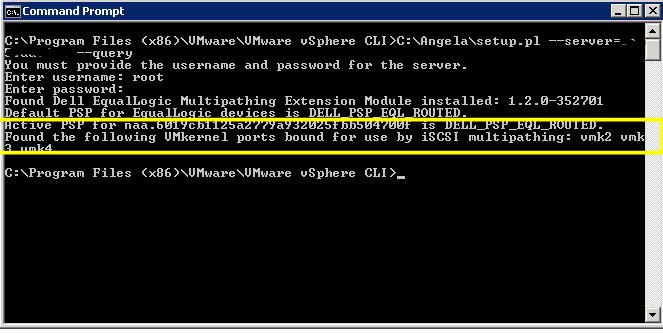
From a system with vMware vSphere CLI installed on it, run the following command to verify the MEM installation. You will need the setup.pl script in order to run it. It’s included in the MEM download.
Enter the following command using your esxi hostname or IP:
# setup.pl --server=esxhostname_or_IP --query
Enter the credentials for the host. After a few moments, the command will display the version of the MEM installed, the default PSP that is now set as well as the vmkernal ports used by MEM.
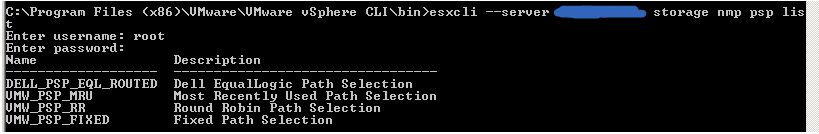
To list the new Dell EQL PSP as well as the defaults, use the following command:
# esxcli --server esxhostname_or_IP storage nmp psp list
Enter the credentials for the host.
Multipathing is available immediately after installation. You can see the paths to the disk as well as the new PSP. On the host, go to the configuration tab+ hardware+storage+right-click the datastore + properties+ managed paths.
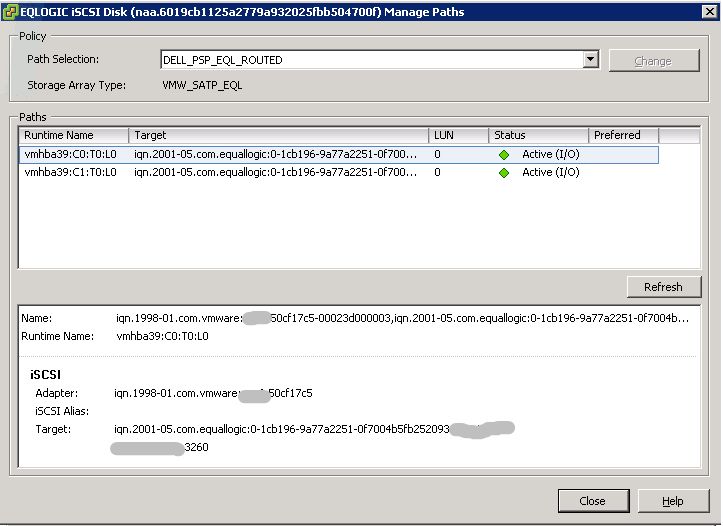
This is what it looked like before the install:
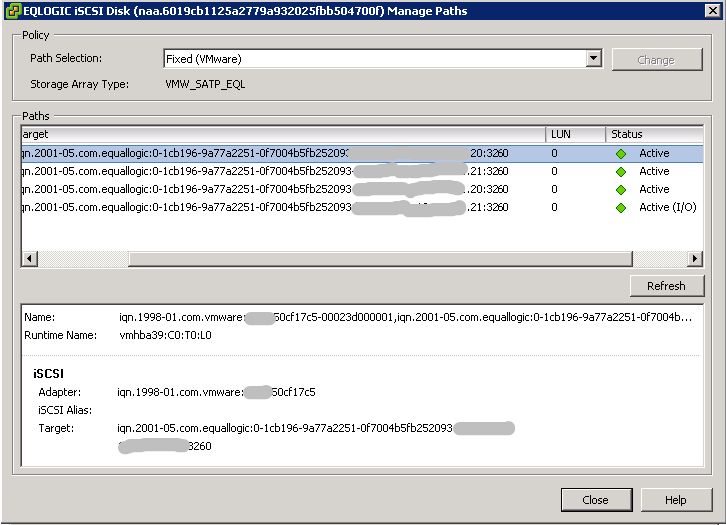
Here you can see that there were 2 active connections to each controller, however, only 1 was being used for I/O. Once MEM is installed, there are redundant active connections to each controller and the load is more evenly balanced.
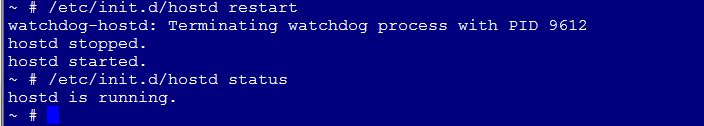
As I mentioned before, the MEM is totally functioning, however, in order to use the new esxcli commands that are available to manage and report on, you’ll have to restart the hostd agent on the esxi host.
Enable SSH on your host and log into it.
Restart the hostd service:
# /etc/init.d/hostd restart
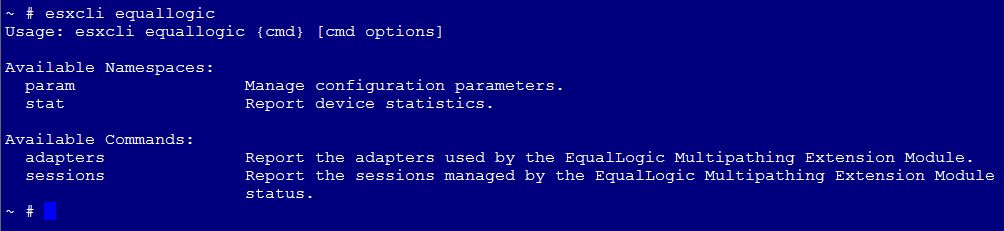
The new commands are now available. To list them:
# esxcli equallogic
Log out of the host and disable SSH.
Done!
For more information on Dell’s MEM, read this great blog post from Cormac Hogan of vMWare.